How to write effective prompts
Understand what an AI prompt is, how it works and how to write ones that get better results.
Last updated on
What is an AI prompt
What you type into an AI tool is called a prompt. A prompt tells the tool what you want it to do. It can be a question or a set of instructions. The tool uses it to decide how to respond.
The way you phrase your request shapes the answer you get. You might get different answers to the same question. Even small changes in wording or order can lead to a different response.
Types of prompts
Type
What it is
Similar to
Best for
Example
A single, direct instruction or question
Giving a command
Getting quick answers with minimal setup
“List 3 ideas for team-building activities.”
A request with one example that shows how you want it done
Saying “Mimic this example”
Generating results that match a specific style
“Write this week’s update. [Update context]
Use the same structure as this: [Example text]”
A request with multiple examples that show a clear pattern or approach
Saying “Notice the pattern across these examples”
Tasks that need closer control over style, layout or logic
“Summarize each section like this: [Example 1], Example 2], [Example 3]. Use the same format.”
A specific set of instructions you can reuse for similar tasks
Filling out a form to guide its response
Getting in-depth, high-quality responses
“Goal: Compare 2 policies
Format: A table with pros and cons
Context: This is for a policy briefing
Constraints: Stick to facts
Voice and tone: Formal
Role: Act like a policy advisor
Supporting documents: [Policy A], [Policy B]”
A back-and-forth dialogue
Talking with a colleague or co-worker
Evolving, complex or open-ended tasks
User: “What are the latest trends in website design?”
AI: [Lists trends like micro-interactions and dark mode]
User: “Tell me more about micro-interactions.”
AI: [Explains hover effects, button animations]
User: “Give me 3 slide titles to explain this.”
AI: [Provides options]
User: “Make them sound more polished.”
Zero-shot prompts
A zero-shot prompt is when you ask AI to do something without giving any examples. You only provide a single instruction or question.
The AI then uses its pre-trained knowledge to respond.
This type of prompt works best for straightforward tasks, like:
- Summarizing short content
- Reformatting text
- Answering basic questions or explaining simple concepts
One-shot prompts
A one-shot prompt includes your request, along with one example of the kind of response you want.
The example helps the AI understand the approach you expect. It reviews your example and uses it as a model when generating its answer. This makes the output more likely to match your intended tone, format or level of detail.
One-shot prompts are useful when:
- You want the response to sound a certain way
- The task could be done in multiple ways, and the example helps narrow the approach
- You want the answer to follow a specific structure
Multi-shot prompts
A multi-shot prompt includes your request, along with multiple examples of the kind of output you want. The more examples you give, the clearer the pattern becomes for the AI. This results in a more reliable response that’s aligned with your needs.
Use a multi-shot prompt when:
- The task involves careful reasoning or logic
- Tone and formatting is important
- The examples show exceptions or edge cases that a single example would not cover
Structured prompts
A structured prompt is a request with a clear layout and instructions. It tells the AI not just what you want, but also how to give the answer.
Think of it like filling out a detailed form for the AI. The more specific you are, the more likely you’ll get a useful and well-organized result. Use this method when you know what you need, you care about how the response is structured and there are multiple requirements to follow.
Parts of a structured prompt

Your goal
What do you want the AI tool to produce?

Your desired format
How should the answer be delivered? For example, in bullet or paragraph form.

Context
What background should the tool consider? For example, “This is for a grade 6 class” or “This is going in a marketing report.”

Constraints
What should the tool avoid in its response? For example, technical jargon or brand names.

Desired voice and tone
What writing style should the tool use? Describe it with adjectives. For example, friendly, formal or neutral. Don’t ask for the style of a public figure, author or published work, like Harry Potter.

What role the tool should take
Whose perspective should the tool adopt? This helps the tool draw on deeper expertise, rather than generic web content. For example, a policy advisor or a help desk agent.

Supporting documents, links, sample text or data
What should the tool base its answer on?
Conversational prompts
Conversational prompting is when you chat with an AI tool like you would with a person.
You don’t need to plan the whole prompt in advance. You can ask the tool one question at a time, then build on the answers.
This style works well when you’re exploring ideas or don’t know exactly what you want yet. It works best for tasks like brainstorming, testing ideas, thinking through a problem or starting something from scratch.
You can begin by asking the tool a broad, general question. From there, build on the response. The sequence will look different for each user. However, in general, you may:
- Ask follow-up questions
- Change direction or angles
- Tell the tool to “try again”
- Provide more context
- Ask the tool to ask you questions until it understands
- Layer in requirements. For example, introducing desired format, audience or constraints in later steps
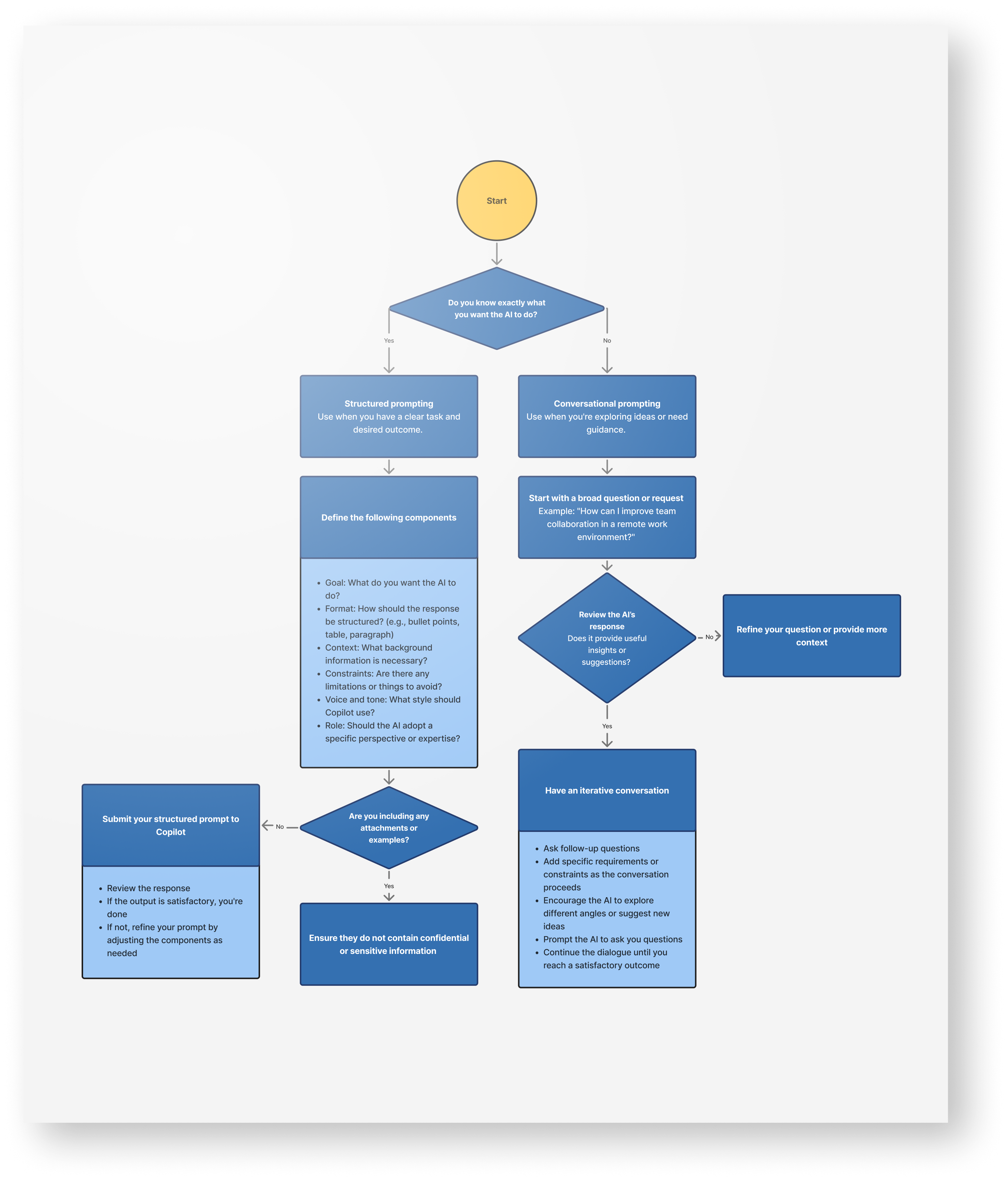
Explore the process
Follow this flow chart to help decide what prompting method will work for you.
How to format your prompts
Many AI tools use a lightweight markup language called Markdown.
It formats text using simple characters and is commonly used in instant messaging applications.
In Markdown, you can show that certain words are emphasized by bolding them. This is done by putting 2 asterisks on each side of the word or phrase. This helps the AI tool understand the structure of your request.
For example:
**Goal**
Write a description of a rock for a museum display.
**Format**
Short factual description that’s suitable for the general public.
**Context**
The rock is igneous. It was found on northern Vancouver Island. It may date to the Late Jurassic period.
How to fine-tune your prompt language
The verb you choose at the start of a prompt tells the AI tool what kind of task you want it to do. Verbs help the AI understand how to respond.
When you use clear verbs, the AI is more likely to produce a useful answer. If you use vague or open-ended phrases, the response might be off-topic, unclear or even made up.
- Weak: What do you think about design?
- Why it’s not strong: AI doesn’t have thoughts or personal opinions. This may lead to hallucination.
- Better: Explain key principles of good user experience design.
- Why it’s better: This directs the AI to narrow its focus on providing factual information instead of guessing what a person might think.
Good prompting is an experiment. Try different verbs to understand what gets you the best results.
Prompting verbs that help you get better results
Task item
Recommended verbs
Creating/drafting
Draft, write, generate, compose
Summarizing/condensing
Summarize, condense, outline, abstract
Explaining/clarifying
Explain, describe, define, illustrate
Analyzing/evaluating
Analyze, assess, evaluate, review
Comparing/contrasting
Compare, contrast, differentiate, distinguish
Suggesting/recommending
Suggest, recommend, propose, advise
Listing/organizing
List, outline, enumerate, structure
Checking/validating
Check, proofread, review, verify
Translating/converting
Translate, convert, rephrase, adapt
Brainstorming/exploring
Brainstorm, explore, ideate, consider
